Infrastructure Setup using Cloud Formation Templates
Services Required to create CICD
- Code Build
- Build code and deploy image in jfrog
- Code Pipeline
- Has (Continuous Integration Continuous Deployment)CICD flow
- Cloud Formation
- To deploy and create infrastructure we use yml files.
- S3
- Store our data packages and yml files which are used by CFT.
- ECS
- To deploy our application on fargate servers
- We can also create our manual EC2 instances from pipeline.
- Secrets Manager
- Manages all the secrets.
- ELB/ALB
- Elastic/Application Load Balancer
- To map context paths of different services
- GitHub
- Stores our code
- Jfrog
- Used to store all the docker images
- Dockerfile
- Used to create a customised docker image
- Scanning for Vulnerabilities free code
- Sonarcube
- Checkmarx
- Twistlock
- Cloudwatch
- Used to store logs
- We create log group for each of instances
- Lambda Functions
- Used for serverless technologies.
Creating a new Environment
- Create the YML images of the different resources required in the environment.
- The CFT templates are stored in S3 or can be uploaded from system.
- Create a new alb one for backend and one for frontend service
- Create a yml file or CFT for alb.
- CFT template is available online on AWS
- ALB contains 2 concepts
- Target Groups
- Listeners
- Parameters define the prerequisites which are needed to create alb these are
- VPC (virtual private cloud)
- Subnets
- ALB security group
- Account number
- Load balancer port
- Health check path
- Certificate
- Load balancer name
- Environment
- UAI
- Resources
- Used for creating resources based on the prerequisites defined in parameters.
- Like creation of Target group, listeners and ALB.
- We define The type of properties of the resource.
- Create target group.
- We give the port(Health check, port and service port).
- Other properties, remain same mostly.
- Creating load balancer.
- Type of load balancer and properties.
- Generally create internal load balancer when we have to expose our services outside.
- Creating listeners
- Listens to the context path exposed by services.
- Context path is added under conditions and values.
- DNS of ALB appended with context path gives us access to that service.
- To update make changes in alb yml and update cloud Formation stack.
- Load balancer hits the service using target groups.
- Each target group is associated with a load balancer and service.
- One load balancer is associated with multiple target groups.
- We can check the different target groups associated with Load balancer in listener and rules section.
- Create security group for alb
- Provides security configuration for our VPC and our resources.
- Has 2 rules
- Inbound rule
- Outbound rule.
- Outbound rules are created automatically.
- Isolates our resources from other resources.
- Create a new cluster
- Cluster is a group of services.
- Create cluster with a defined name.
- Update the security group with the micro service port number.
- Create cloud watch log group.
- Log groups are used to monitor logs of service.
- If we don’t have log groups, deployment will not happen.
- Log groups can be created from CFT template.
- Create Target Group for that micro-service.
- Creating services
- Before creating service, kindly ensure we have created log group cluster.
- Every service has a task definition, cluster and load balancer which needs to be created first.
- We need to create a stack from cloud formation for creating each of the service like code build, code pipeline ,ecs sevices, cluster etc.
- Creating code build project
- Create CFT for code build project and code pipeline and deploy it on cloud Formation to create code build and code pipeline for that microservice.
- Stages of code build
- Pre Build
- Build
- Post Build
- Define the buildspec file which defines initial configuration parameters.
- Define the git repository from which code needs to be pulled from.
- Creates a package by building code from git and will create an image using docker file.
- Takes care of continuous integration(CI) process.
- Perform code scanning, such as checkmarks et cetera.
- Upload the image to repository like JFrog/NEXU
- Look’s for build spec file in root directory of project.
- Create new code pipeline
- Creates service from the image created by code build(Creates a task definition).
- Deploy the cluster as one of the service.
- We can define code pipeline to trigger whenever there is a change in bucket/file in the bucket.
- This change can be done from buildspec file.
- Thus once the code build Has done creating and uploading image. We can trigger the pipeline by updating parameter of pipeline to S3 bucket.
- First time a change set is created for service then in every sequential runs the change set is updated for service.
- Enabling web hook
- Edit source of code build project.
- Disable “Allow AWS code build to modify this service role so that it can be used within this build project.”
- Select “ Rebuild Every time a code change is pushed to this repository”.
- Select the desired webhook event.
- Add the branch to pull from in HEAD_REF under “ start a build under these conditions”.
- Click Update Source.
- Once we update source, we get a payload URL and secret.
- Add the payload URL and secret to GitHub configuration settings.
- While creating/updating a stack ensure to check change in parameters in changeset in last step, specially the replacement option which replaces the old resource.
- Creation of task is done using task definition.
- Task definition details they need to update in lambda definition.
- They need to give the ARN of task definition.
- Cloud formation output goes to secret manager parameters for lambda function and ARN update.
- Enable webhook to create code build project.
- Enable ddi for the alb for both backend and fronted.
- Create Docker File
- Used to create a customisable docker image.
- “From” parameter defines the type of machine of the docker image.
- “ARG” defines command to be run on that image.
- “COPY” define if we need to create copy of file.
- “Entrypoint” Defines a command which continues to execute in docker example an executable.
- Runs once Container is launched from an image.
- Create parameter's file, and settings.yml file
- Create buildspec.yml file.
- Buildspec.yml is read by codebuild.
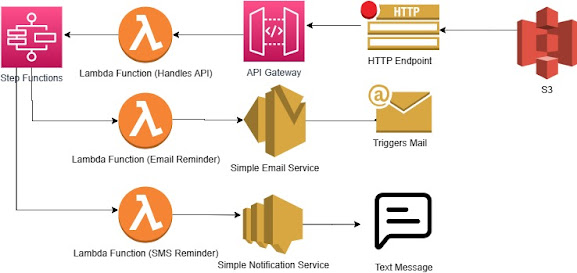
- Creating a step function and task definition.
- Sometimes we need to run tasks out of the scope of Application session For example, performing An ETL.
- We use scripts that run Outside the application to perform such tasks.
- To run these scripts We may require task definitions that are needed Only when these scripts are being executed.
- We can create a step function to Call task definitions If we want to perform some dedicated tasks using scripts separately.
- For example, to extract data from a Python script, we can create A step function Which will call a task definition which in-turn calls the python script.
- Tasks which take longer time may be called using task definitions.
- We create a CFT which creates a task definition and a state machine Which runs the task definition.
Infrastructure setup using Cloud Formation Templates
- Add XML, JSON, YML templates to S3 and CFT reads those from CFT and creates Components accordingly.
- Create code build from CFT.
- Configure code build webhook To pull code From the code sub-versioning system like GIT/SVN.
- Create code pipeline from CFT.
- Integrate code build with code pipeline by polling or Manual hit Using CFT templates.
Cloud Formation Templates
Following are some examples of cloud formation templates in json format
{
"AWSTemplateFormatVersion" : "2010-09-09",
"Description" : "this template does XXXX",
"Metadata" : {
},
"Parameters" : {
},
"Mappings" : {
},
"Conditions" : {
},
"Transform" : {
},
"Resources" : {
},
"Outputs" : {
}
}
Following are some examples of cloud formation templates in yml format
---
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Description:
this template does XXXX
Metadata:
template metadata
Parameters:
set of parameters
Mappings:
set of mappings
Conditions:
set of conditions
Transform:
set of transforms
Resources:
set of resources
Outputs:
set of outputs
{
"Resources": {
"mypics": {
"Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket"
}
}
}
{
"Resources": {
"mypics": {
"Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket"
},
"taggedpics": {
"Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket"
}
}
}
{
"Resources": {
"mypics": {
"Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"Properties": {
"BucketName": "myawesomepicsfdsfdsfdscxvcxv"
}
},
"familypics": {
"Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket"
}
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment